apan has been experiencing severe water-related disasters almost every year due to active rain fronts and large typhoons passing by or through the archipelago. In some events, small and medium-sized rivers flood with a large volume of water, sediment, and driftwood. As climate change is anticipated to progress, the government has been reviewing the basic policy for river development and planning various measures, including many river dredging projects to secure adequate river cross-sectional area.
Under these circumstances, there is an increasing need for methods to evaluate sediment transport in rivers and the accompanying changes in riverbeds. However, there are limited methods available to evaluate water-related hazards, such as sediment-driftwood-water flooding, which include areal sediment transport in the basin, according to various spatiotemporal scales covering normal and flood times.
To develop a sediment hydrological model that can handle various spatiotemporal scales ranging from structures to basins and predict water-related hazards, including sediment-driftwood-water flooding. To use the developed sediment hydrological model to practice effective river management by applying it to various river basins.
FY2022-FY2027
| Chief Researcher | KUBOTA Keijiro |
| Senior Researcher | TANAKA Yozo |
| Research Specialists | HARADA Daisuke, Qin Menglu, Kattia Rubí Arnez Ferrel |
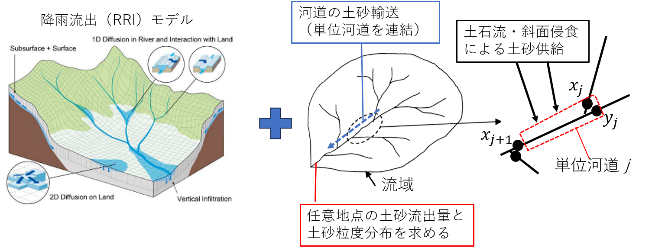
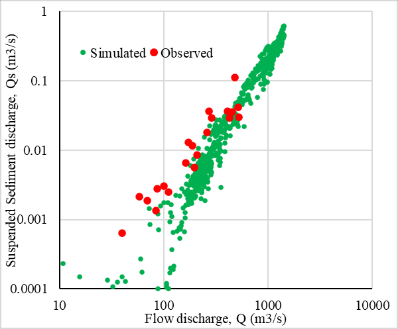
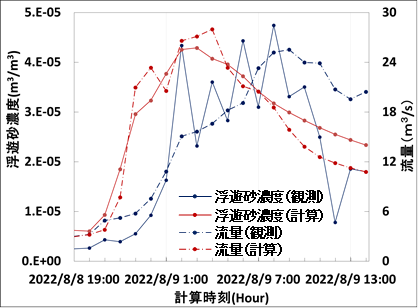
Our project aims to develop a sediment hydrological model capable of processing basin, two-dimensional, and three-dimensional data. This research is particularly dedicated to developing the Rainfall-Sediment-Runoff (RSR) model for simultaneously analyzing the basin-scale transportation of water, sediment, and driftwood. This model should be capable of providing time-series data on sediment volume, sediment particle size, and driftwood runoff at a given point of the basin. We are currently examining the model’s applicability by testing it on different river basins in Japan and abroad.